New Design Regions
A design region is a compact subset of $\Reals^{\DimDesignRegion}$. In code, it is represented by a subtype of Kirstine.DesignRegion, which takes a type parameter N that corresponds to the dimension $\DimDesignRegion$ above.
The package implements DesignIntervals, which are N-dimensional boxes with sides parallel to the coordinate axes. This vignette describes how to implement your own subtype of Kirstine.DesignRegion.
Our example will be axis-parallel ellipsoidal subsets of $\Reals^{\DimDesignRegion}$. (Note that this could alternatively be achieved with a DesignInterval and a suitable coordinate transformation in the Kirstine.CovariateParameterization.)
Implementation
Apart from the subtype of Kirstine.DesignRegion{N}, the following methods must be implemented:
boundingboxis used in several places.isinsideis used in several places.dimnamesis used for plotting.random_designpoint!is used in the initialization step of a particle-based optimizer.move_designpoint_how_faris used in the movement step of a particle-based optimizer.move_designpoint!does the actual moving.
using Kirstine
struct DesignEllipsoid{N} <: Kirstine.DesignRegion{N}
name::NTuple{N,Symbol}
center::NTuple{N,Float64}
semiaxis::NTuple{N,Float64}
end
# return the lower bound and upper bound of a box enclosing dr
function Kirstine.boundingbox(dr::DesignEllipsoid)
return dr.center .- dr.semiaxis, dr.center .+ dr.semiaxis
end
# return true iff dp is inside (or on the boundary) of dr
function Kirstine.isinside(dp, dr::DesignEllipsoid)
# check without implicitly allocating a new vector
acc = 0.0
for i in 1:length(dp)
acc += ((dp[i] - dr.center[i]) / dr.semiaxis[i])^2
end
return acc <= 1
end
Kirstine.dimnames(dr::DesignEllipsoid) = dr.name
function Kirstine.random_designpoint!(dp::AbstractVector{<:Real}, dr::DesignEllipsoid)
# start outside, then rejection sample from closed unit ball
# (this could be made more efficient)
dp .= 1
while (sum(x -> x^2, dp) > 1)
rand!(dp)
dp .*= 2
dp .-= 1
end
# scale and translate
dp .*= dr.semiaxis
dp .+= dr.center
return dp
end
# If p+v is inside dr, return 1.
# Else find the smallest t >= 0 such that p + tv is on the boundary of dr.
function Kirstine.move_designpoint_how_far(dp, v, dr::DesignEllipsoid{N}) where N
t = 1.0
if sum(i -> ((dp[i] + t * v[i] - dr.center[i]) / dr.semiaxis[i])^2, 1:N) > 1
# solve quadratic equation
a = t^2 * sum(i -> (v[i] / dr.semiaxis[i])^2, 1:N)
b = 2 * t * sum(i -> (v[i] * (dp[i] - dr.center[i])) / (dr.semiaxis[i]^2), 1:N)
c = sum(i -> ((dp[i] - dr.center[i]) / dr.semiaxis[i])^2, 1:N) - 1
t = (-b + sqrt(b^2 - 4 * a * c)) / (2 * a)
end
return t
end
# Move dp to dp + t * v,
# and make sure that the result numerically stays inside or on the boundary of dr.
function Kirstine.move_designpoint!(dp, t, v, dr::DesignEllipsoid{N}) where N
dp .+= t .* v
# sometimes we numerically land just outside the boundary,
# go a bit back inside in such a case
while !(Kirstine.isinside(dp, dr))
dp .-= 0.01 .* t .* v
end
# sometimes we are still a bit outside along the semiaxes,
# which we fix here
dp .= min.(max.(dp, dr.center .- dr.semiaxis), dr.center .+ dr.semiaxis)
return dp
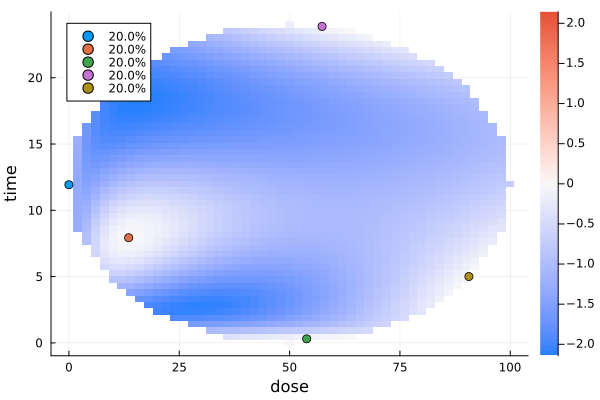
endExample
To see the new region in action, we will reuse the dose-time-response example. Instead of the design interval
\[\DesignRegion = [0, 100] × [0, 24]\]
that was used there, we will take an ellipse centered at $(5, 12)$ with semi-axis lengths $(5, 12)$, i.e. with the interval above as its bounding box.
using Random, Plots
@kwdef struct DTRMod <: Kirstine.NonlinearRegression
sigma::Float64
m::Int64
end
mutable struct DoseTimeCovariate <: Kirstine.Covariate
dose::Float64
time::Vector{Float64}
end
Kirstine.unit_length(m::DTRMod) = m.m
function Kirstine.update_model_vcov!(s, m::DTRMod, c::DoseTimeCovariate)
fill!(s, 0.0)
for j in 1:(m.m)
s[j, j] = m.sigma^2
end
end
Kirstine.allocate_covariate(m::DTRMod) = DoseTimeCovariate(0, zeros(m.m))
@simple_parameter DTR a e e0 emax ec50
function Kirstine.jacobianmatrix!(jm, m::DTRMod, c::DoseTimeCovariate, p::DTRParameter)
for j in 1:length(c.time)
A = exp(-p.a * c.time[j]) # calculate exponentials only once
B = exp(-p.e * c.time[j])
C = B - A
rd = p.e - p.a # rate difference
den = c.dose * C * p.a - rd * p.ec50
den2 = den^2
# ∂a
jm[j, 1] = -c.dose * p.ec50 * p.emax * (A * c.time[j] * p.a * rd + p.e * C) / den2
# ∂e
jm[j, 2] = c.dose * p.a * p.ec50 * p.emax * (B * c.time[j] * rd + C) / den2
# ∂e0
jm[j, 3] = 1.0
# ∂emax
jm[j, 4] = c.dose * p.a * C / den
# ∂ec50
jm[j, 5] = c.dose * p.a * p.emax * C * rd / den2
end
return jm
end
function draw_from_prior(n)
pars = map(
0.5 .+ 0.10 .* randn(n),
0.1 .+ 0.02 .* randn(n),
1.0 .+ 0.25 .* randn(n),
2.0 .+ 0.50 .* randn(n),
exp.(2.3 .+ 0.6 .* randn(n)),
) do a, e, e0, emax, ec50
return DTRParameter(a = a, e = e, e0 = e0, emax = emax, ec50 = ec50)
end
return PriorSample(pars)
end
Random.seed!(4711)
prior = draw_from_prior(1000)
struct CopyBoth <: Kirstine.CovariateParameterization end
function Kirstine.map_to_covariate!(c::DoseTimeCovariate, dp, m::DTRMod, cp::CopyBoth)
c.dose = dp[1]
c.time[1] = dp[2]
return c
end
dp1 = DesignProblem(
criterion = DCriterion(),
region = DesignEllipsoid((:dose, :time), (50.0, 12.0), (50.0, 12.0)),
model = DTRMod(sigma = 1, m = 1),
covariate_parameterization = CopyBoth(),
prior_knowledge = prior,
)
Random.seed!(1357)
st1 = DirectMaximization(
optimizer = Pso(swarmsize = 30, iterations = 50),
prototype = uniform_design([[25, 6], [25, 18], [50, 12], [75, 6], [75, 18]]),
fixedweights = 1:5,
)
Random.seed!(2468)
s1, r1 = solve(dp1, st1)
gd1 = plot_gateauxderivative(s1, dp1)